Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.933 - 941, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have investigated profile formation and sustainment of current hole (CH) plasma by 1.5D transport simulations with current limit model inside CH based on Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium. Sharp reduction of anomalous transport in RS region can reproduce JT-60U experiments. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in autonomous profile formation of ITB and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling. The scaling means that core plasma inside ITB is governed by MHD equilibrium limit, i.e., autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to penetration of inductive current. This shrink is prevented and CH size can be controlled by appropriate external CD. CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD. Application of CH plasma to reactor is discussed.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
Profile formation and sustainment of tokamak plasmas with current hole (CH) have been investigated by using 1.5D transport simulations. A current limit model inside CH based on the Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium is introduced. We found that the sharp reduction of anomalous transport in the reversed-shear (RS) region can reproduce JT-60U experiment. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in the autonomous formation of internal transport barrier (ITB) and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling, which means autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with the full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to inductive current penetration. This shrink is prevented and the CH size can be controlled by appropriate external current drive (CD). The CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD.
Li, J.; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 11(4), p.1493 - 1510, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:85.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The electron temperature gradient (ETG) driven turbulence in tokamak core plasmas is numerically investigated based on three-dimensional gyrofluid model with adiabatic ion response. Attentions are focused on the zonal flow dynamics in ETG fluctuations and the resultant electron heat transport. A high electron energy confinement mode is found in the weak magnetic shear regime, which is closely relevant with self-organization behavior of turbulence through the enhanced zonal flow dynamics rather than the weak shear stabilization of ETG fluctuations. It is demonstrated that the weak shear is favorable for the enhancement of zonal flows in ETG turbulence.
Takizuka, Tomonori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(12), p.1282 - 1284, 2002/12
An idea of a new equilibrium of a strongly-reversed-shear tokamak plasma with a current hole is proposed. This equilibrium configuration called "Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands (ATMI) equilibrium" has three islands, a central-negative-current island and side-positive-current islands, along the R direction and two x-points along the Z direction. The equilibrium is stable with the elongation coils when the current in the ATMI region is limited small.
Smolyakov, A. I.; Lazzaro, E.*; Coelho, R.*; Ozeki, Takahisa
Physics of Plasmas, 9(1), p.371 - 374, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:27.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Proceedings of 29th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 4 Pages, 2002/00
This paper presents the feasibility and issues of steady state operation with a central current hole for JT-60SC, the superconducting tokamak to be modified from JT-60, from the view of reactor applicability of the current hole. An impact of the current hole on fusion engineering would stand in no necessity of central current drive leading to a remarkable reduction of neutral beam injection energy. The 1.5D time-dependent transport code analysis is made with using thermal and particle transport coefficients deduced from observations in JT-60U as a function of the magnetic shear. A steady state operation with HHy2~1.6 and beta_N~4 is obtained at Ip=1.5 MA, Bt=2 T and q95=4.5 by off-axis beams of 11.2 MW. The bootstrap fraction of ~75% of the plasma current and the current hole region of ~30% of the minor radius are sustained up to 70 s. The results suggest that a bootstrap current evolution near the current hole region and a relation between the location of ITB and the central current hole region are important to achieve a steady state plasma compatible with the current hole.
Hatae, Takaki; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Australia Workshop on Plasma Diagnostics (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2002/00
The main purpose of JT-60U project is to make contribution to establishment of scientific basis of ITER and the demo tokamak reactor. Our ultimate goal is to achieve and sustain high integrated performance, namely high beta, high confinement, high bootstrap current fraction, full non-inductive current drive and heat/particle control, in a reactor-relevant regime. Toward this goal, we have developed weak magnetic shear ("high 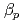 mode") and reversed magnetic shear plasmas. In both regimes, the internal transport barrier (ITB) and the edge pedestal are obtained simultaneously. As a large-sized tokamak equipped with a variety of devices for heating, current drive and profile control, JT-60U has high ability to approach the conditions required in reactors (ITER or demo): low values of normalized Larmor radius and collisionality, high toroidal field, high temperature with Te
mode") and reversed magnetic shear plasmas. In both regimes, the internal transport barrier (ITB) and the edge pedestal are obtained simultaneously. As a large-sized tokamak equipped with a variety of devices for heating, current drive and profile control, JT-60U has high ability to approach the conditions required in reactors (ITER or demo): low values of normalized Larmor radius and collisionality, high toroidal field, high temperature with Te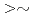 Ti, small central fueling, small ELM activities, etc. This paper reviews recent JT-60U results with the emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime.
Ti, small central fueling, small ELM activities, etc. This paper reviews recent JT-60U results with the emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime.
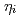 mode and effects of plasma rotation shear in weak magnetic shear region
mode and effects of plasma rotation shear in weak magnetic shear regionLi, J.; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Tsuda, Takashi
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 42(4), p.443 - 453, 2000/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; *
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 40(9), p.1673 - 1678, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.04(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; *; M.Elia*
Physics of Plasmas, 4(11), p.4031 - 4034, 1997/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; *; M.Elia*
PPL-167, p.1 - 13, 1997/08
no abstracts in English
Kishimoto, Yasuaki; J.Y.Kim*; Tajima, Toshiki*; W.Horton*; J.Furnish*
Theory of Fusion Plasmas, ISPP17, p.213 - 226, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Tokuda, Shinji; *
JAERI-Research 96-057, 62 Pages, 1996/11
no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
Nuclear Fusion, 35(10), p.1225 - 1230, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
; *;
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 50(2), p.655 - 658, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:53.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 plasma in sheared magnetic field
plasma in sheared magnetic field*; ; *
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 48(3), p.973 - 982, 1980/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:70.74(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; *
Phys.Fluids, 23(4), P. 847, 1980/00
no abstracts in English